|
KOREA FOREIGN LABOR POLICIES
|
|
|
| 1. Employment system for professional . skilled foreign workers |
|
 Overview Overview |
|
| |
Pursuant to the Immigration Control Act, professional or skilled foreigners can be employed in Korea after being issued
with the following types of visas : professors(E-1), teaching foreign languages(E-2), research(E-3), special technology instruction(E-4),
specialty occupations(E-5), arts and entertainment(E-6), and other particular occupations(E-7). For IT workers in particular,
the gold card system was introduced in November, 2000 and has been implemented since then. The gold card system is intended
to relax requirements for the stay of IT workers in Korea by issuing multiple visas, extending maximum sojourn periods and
permitting activities other than those permitted under their status of sojourn. | |
|
 Eligible people Eligible people |
|
 |
General procedure : The parties concerned sign an employment contract. à A related minister makes a recommendation. à
The Minister of Justice issues a visa issuance certificate. à The foreign worker enters Korea. Arts and entertainment (E-6)
: A performance company requests a performance. à The entertainment agent and the entertainer sign an employment contract.
à The agent asks the performance to be deliberated and recommended. à The Korea Media Rating Board makes the deliberation
and recommendation. à The Minister of Justice issues a visa issuance certificate. à The entertainer concerned enters Korea.
|
|
 |
When the Korea Media Rating Board recommends a performance by a foreign entertainer, the Performance Act should be applied.
And only worker dispatch agents under the Act on Protection, etc. for Dispatched Workers can apply for the recommendation
of a performance. |
|
 |
Under the Act on Protection, etc. for Dispatched Workers, "arts and entertainment" are included in 26 occupations for which
worker dispatch is permitted.
| 2.Industrial trainee system |
|
 Overview Overview |
|
| |
The industrial trainee system was introduced in 1993 based on the Immigration Control Act. At the time of introduction,
it was a two-year training program, but in December 2001, it was transformed into an one-year training and two-year employment
program which took effect from April 18, 2002. Under this system, if foreign industrial trainees have passed a certain technical
qualification test or completed employment training, they are allowed to be employed as workers for two years. | |
|
 Implementation procedure Implementation procedure |
|
| |
To get further information on the industrial trainee system, please visit the Korea Federation of Small and Medium Business'
website (www.kfsb.or.kr). |
| 3. Employment management system |
|
 Overview Overview |
|
| |
| General eligibility |
The service-sector employment management system which allows ethnic Koreans of foreign nationality to
work in Korea for two years was introduced on December 9, 2002 in order to reduce labor shortages in the service sector and
meet the demand of ethnic Koreans of foreign nationality.
Ethnic Koreans of foreign nationality, issued with a visit-and-cohabitation
visa (F-1-4), are allowed to enter Korea. Among them, those who have signed an employment contract using a standard labor
contract form are placed in jobs through job placement services by employment security centers under the Ministry of Labor. | | | |
|
 Those eligible for visitation and cohabitation visas permitting employment Those eligible for visitation and cohabitation visas permitting employment
|
|
| |
To get further information on the industrial trainee system, please visit the Korea Federation of Small and Medium Business'
website (www.kfsb.or.kr). | |
|
| |
| special eligibility |
Eligible people are ethnic Koreans of foreign nationality aged 30 or older who have 8th degree or closer
paternal relatives or 4th degree or closer maternal relatives in Korea, who are listed on Korea's census register, or who
are lineal ascendants or descendants of those listed.( 8th degree or closer paternal relatives or 4th degree or closer maternal
relatives of ethnic Chinese who have acquired Korean nationality after the establishment of diplomatic ties between Korean
and China are also eligible.)
1. lineal paternal relatives of persons who did distinguished services to independence
2.
persons considered having largely contributed to sound development of overseas Korean communities
3. persons who entered
Korea as industrial trainees and then returned home without running away from their workplaces
4. persons specially recognized
by the Minister of Justice
| | | |
|
 Permitted types of occupations and the size of permission Permitted types of occupations and the size of permission |
|
| |
| special eligibility |
The types of occupations for which employment is permitted and the size of permission are determined based
on the state of illegal employment. But it is limitedly permitted and additional permission in terms of types of occupations
and size during 2003 is considered.
The total number of ethnic Koreans to be introduced is 50,000. Beginning from December
2002, the first batch of 25,000 has been imported and the rest will be imported given the number of departed illegal workers.
| | | | |
|
| | |

EPS and Other Labor Policies, MOL, MOJ notices
| Overview |
| 1.Definition of Employment Permit System for Foreigners |
 |
The Employment Permit System allow employers who have failed to hire native workers to
legally hire an adequate number of foreign workers and is an system that the government uses to introduce and manage foreign
workers in Korea in an organized manner.
 |
Construct efficient employment management system for foreign
workers |
 |
Apply identical labor conditions and human rights as the native workers |
 |
To prevent absurdity, the government selects and invites foreign workers
|
|
 |
Most countries, short of manpower due to economy development and aging society, are introducing legal employment
of foreign workers. |
|
| 2.Permitted category of business for foreign workers |
 |
Under the Foreign Employment Permit, foreign workers are restricted to be only allowed
to work in 5 business industries.
 |
Manufacturing Industry, Construction Industry, Agriculture and Stockbreeding (Farm Products
Cultivation, Stockbreeding), Fishing Industry, Service Industry (Refrigerated Warehousing, Restaurants, Business Support Service,
Social Welfare, Sewage Disposal, General Repair Services of Motor Vehicles, Nursing, Household Service etc.) | | |
| 3.Legal Position of Foreign Workers |
 |
Foreign workers are applied with the labor related laws during the period of employment
identical to the native workers such as Labor Standard Act, Minimum Wages Act, Industrial Safety Health Act etc.
| - |
Household service workers are not applied with labor laws. The employer can decide and enforce
all the labor conditions including labor time, dismissal, off day, holiday within enforcement regulations of the Civil Law
Act. |
| - |
Some provisions of relevant regulations are not applied to foreign workers in agriculture, forestry,
and fisheries industry.
 |
For example : Foreign workers in agriculture, stockbreeding, fisheries industry are not applied
with the "Regulations for Additional Wages" (Extension and holiday work) of the Labor Standard Act. | | | | |
|
| |
| |
| |
|
|
| |
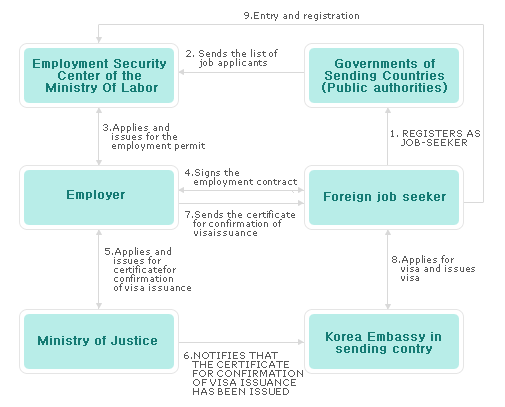
| 1.Prepare list of candidate workers (Applying for job) |
 |
In case a foreign worker from a sending country wishes to be employed in Korea under
the EPS, the person needs to fill out an application form at a sending agency and must satisfy the following requirements.
 |
Over 18 of age, proved healthy through the medical examination, identity without any reason
for disqualification (Without any reason for disqualification in entering Korea based on Immigration Control Law)
| |
 |
Other rules regarding job application
 |
In case a job-seeker fails to sign a labor contract in a year after being included in the
job-seekers list, or provides false information, the person will be excluded from the list. |
 |
For the reasons such as 1 year of not concluding labor contract after being registered on the job application
list, giving false statement can exclude the applicant from the job application list. |
 |
Being included in the list doesn't necessarily guarantee employment in Korea. Korean employers choose
workers they need from the list. | | |
| 2.Concluding Labor Contract |
 |
Labor contract must be concluded with the selected foreign workers within 3 months
of the issuance of the Employment Permit.
| - |
Immigration work such as concluding labor contracts, application of a Certificate for Confirmation
of Visa Issuance, and the entry of foreign workers can be entrusted to non-profit corporations such as HRD Korea.
| |
 |
When concluding a labor contract, a standard labor contract form must be used and a labor
contract is regarded completed when employers send one of two original copies to a foreign worker in question after filling
them out and the worker signs it. |
 |
Labor contract period can not exceed 1 year and can be renewed within the limit of 3 years
from the entry date to Korea. | |
 |
Labor contract is valid from the date of the entry of the foreign worker.
 |
Date of the beginning of the contract stated on the Labor Contract and the actual date of
entry can be different (Labor contract valid date) |
 |
In case of labor contract renewal, foreign worker must receive permission for extending before the expiration date. (Article
25, Immigration Control Law) | |
| 3.Applying for Certificate for Visa Issuance and Entry of the Foreign Workers |
 |
Applying for Certificate for Visa Issuance
 |
User who have concluded labor contract with the foreign worker must apply for certificate
for visa issuance to the local Exit and Entry Control Bureau to bring the foreign workers into the country. Must send to the
foreign worker to help them proceed with the entry procedures in the Korean legation. |
 |
Foreign workers who have received the certificate for Visa issuance must apply for Visa issuance
to the Korean Legation of the country of the residence. The foreign worker must be issued with E-9 visa and enter Korea in
the scheduled date. | | |
| 4.Employment Training for Foreign Workers |
 |
Employment Training
 |
A foreign worker shall be transferred to a preemployment center from the airport upon
arrival to receive preemployment training. Preemployment training is regarded as providing labor under the Labor Standards
Act.
| - |
Preemployment training agencies vary by country.
 HRD Korea(Indonesia, Philippines, Thailand, Sri Lanka) HRD Korea(Indonesia, Philippines, Thailand, Sri Lanka)
 koilaf(Mongolia, Vietnam) koilaf(Mongolia, Vietnam)
| |
 |
Preemployment training programs are for 3 or 4 days and the curriculum consists of training
and labor law aimed to help foreign workers adjust to Korea. Employers pay the training cost. |
 |
For efficient management, foreign workers are guided to the Employment education institute.
During the education period, foreign workers receive medical examination based on the clause 1 article 100, Industrial Safety
Health Act. The workers are guided to the business proprietor after completing the employment education. | | |
 B. Special Employment in Service Industry B. Special Employment in Service Industry |

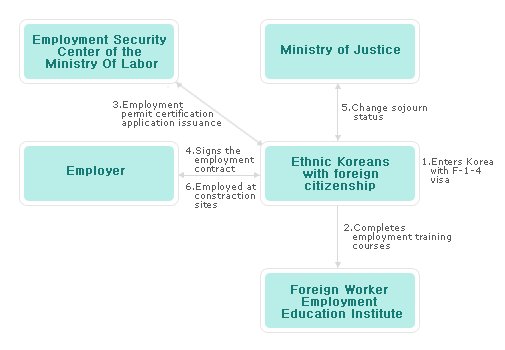
| 5.Special Employment |
 |
Eligibility
| - |
F-1 holders who complete the preemployment training for foreign workers can apply for a job
at an employment security center and get employed by getting job placement(service) and employment permit(construction) issued
by the centers
|
| - |
In case a labor contract is signed, workers in question shall change their visa status of stay into E-9 at the Immigration
Office | |
 |
Completing preemployment training
| - |
Foreign workers who wish to get employed in service or construction may apply for preemployment
training after alien registration at the Ministry of Labor upon arrival. |
| - |
Preemployment training cost shall be paid by foreign workers in question |
| - |
In particular, special employment of foreign workers in the construction industry requires certain education set by the
Minister of Labor in addition to preemployment training for foreign workers. | | |
|
| Important Notice for Foreign Workers |
| 1.Permission for Change of Business or workplace |
 |
In principle, foreign workers are not allowed to change business or workplace |
 |
Yet for the reasons below, in case the worker is difficult to maintain normal labor relationship
with the business or within the work place, the worker may ask permission for change of business or workplace. |
| < Reasons allowing foreign workers to ask permission for change of business > |
| |
| - |
In case the user would prefer to terminate the labor contract period for justful reason.
In case of the refusing to renewal after the labor contract has been expired.
 'Justful reason' means being terminated of the contract due to difficulty in business 'Justful reason' means being terminated of the contract due to difficulty in business
management or
due to worker's fault etc. |
| - |
In case it is not possible to continue to work in the business due to reasons not of the foreign workers
faults such as shutdowns and abolishment of business. |
| - |
In case the business receives orders to cancel foreign worker employment permit or measures to restrict
employment. |
| - |
In case the foreign worker is unable to work in a certain business or workplace, for example having injury
and has no problem in changing workplace. | |
| |
 |
In case reasons for workplace change occur, Foreign workers must apply for workplace change
at a local employment security center within one months after the termination of labor contract in case justifiable reasons
occur.
 |
Foreign workers have to depart in case they fail to apply for workplace change within one
month after the termination of labor contract or fail to receive an approval of workplace change according to Article 21 of
the Immigration Control Act within 2 months after the date of application. | |
| - |
Foreign worker can not apply to change workplace more than 3 times during terms of stay. Only in case
the worker can not stay at a certain business due to reasons not responsible of the foreign worker such as closing or quitting
business, and only in cases when employment permission has been cancelled due to accidents and that the business has been
changed 3 times already, foreign worker is allowed to apply for one more additional change. |
| - |
Changing business of the foreign workers are strictly restricted |
| 2.Insurance and Trust |
 |
To protect rights and to induce voluntary departure of foreign workers who enter Korea under
the EPS, employers shall provide departure guarantee insurance and delayed payment insurance to workers and workers shall
insure themselves for return cost insurance and accident insurance. |
 |
As soon as entering Korea, foreign workers are insured of Employment Insurance, Health Insurance
by the business, and must become insured to Return Cost Insurance and Trust, Accident Insurance etc..(insure during preemployment
training period) |
 |
Accident insurance is to insure workers against injuries, or disease beyond work-related
accidents and to compensate deaths or injuries of workers
| - |
Target for Insurance and Insured person : Foreign Workers |
| - |
Time due for Insurance : Within 15 days of valid date of the labor contract
 |
If not applied, must pay penalty upto 5 million Korean won. | | |
 |
Insuring workers and insurance claims
| - |
Foreign worker must pay the price decided by the Minister of Labor at one time, premium vary
by age or gender |
| - |
In case foreign workers die or get injured due to reasons other than work-related accidents, insurance
payment will be made as notified by the Minister of Labor
|
| - |
Insurance claims can be filed by foreign workers themselves or surviving family to HRD Korea(headquarters).
 |
Obligatory to insure Accident Insurance nevertheless insured to Accident Compensation Insurance
from the workplace.
| | |
| < Return Cost Insurance and Trust > |
 |
Return guarantee insurance is for a lump-sum payment to cover return cost and paid when foreign
workers depart.
| - |
Target for Insurance and Insured person : Foreign Worker |
| - |
Time due for Insurance : Within 80 days of valid date of the labor contract
 |
If not applied, must pay fine of 1 million Korean won. | | |
 |
Insuring workers and insurance claims
| - |
Foreign worker must pay at one time the amount notified by the Minister of Labor different
for each country considering the return cost. |
| - |
Foreign workers can claim insurance money from HRD Korea for following reasons and in case foreign
workers in question are deceased, surviving family members can claim it.
 |
Reason for applying for the money of Return Cost Insurance and Trust
 In case of departure due to termination of contract term. In case of departure due to termination of contract term.
 In case of departing before the termination of contract term. In case of departing before the termination of contract term.
(except for temporary departure)
 In case the foreign worker who has left from the workplace, volunteered to depart In case the foreign worker who has left from the workplace, volunteered to depart
or being departed by
force.
| | |
 |
Employers who use foreign workers must subscribe to departure guarantee insurance and payment
delay insurance |
| < Departure Guarantee Insurance and Trust > |
 |
Departure guarantee insurance is for employers to guarantee the severance money under the Labor
Standards Act. This is for workers who worked at least for one year at business with 5 or more workers |
 |
Target for Insurance
| - |
Business proprietor of industry of 5 or more regular workers, that are employing foreign
workers |
| - |
Business proprietor employing foreign workers with 1 or more year of terms of stay (except Special
Employment in Construction Industry)
 |
Foreign workers working for business workplace are the Insured person or beneficiary. | | |
 |
Terms of Insurance : Within 80 days of valid date of the labor contract
| - |
Effective date of a labor contract means the first entry date of foreign workers. For
foreign workers whose visa status was changed, it is the date they got the approval(privileged workers). For foreign workers
who have already entered and changed workplace or extended the visa status of stay, it means the date when they received the
approval.
 |
If not applied, must pay penalty upto 5 million Korean won. | | |
 |
Insuring workers and insurance claims
| - |
The amount decided by the Minister of Labor is reserved separately from wages
 |
8.3% of monthly average wage of Employment Permit | |
| - |
Foreign workers departing after the expiration of 1 or more years of contract terms without any leaving
of the workplace, foreign workers can directly claim a lump sum payment | |
 |
Others
| - |
However, in case the foreign workers having left the workplace or changed business within
1 year of employment or departure (except temporary departure), the amount is valued to the user. |
| - |
Claim for Departure Guarantee Insurance and Trust are inalienable and cannot be used as collateral | |
| < Delayed Payment Insurance > |
 |
Payment delay insurance is an insurance for employers against delay in payment. Insurance
money is paid in case employers delay in payment. |
 |
Target for Insurance (except for business of special employment in construction industry)
| - |
Business or workplace not applied of Wage and Bond Security Law |
| - |
Business or workplace of 300 or less regular workers
 |
Business not applied with Wage and Bond Security law
 |
Any one except housing construction workers, construction workers, electricians, information
technology engineers, fire facilities engineers, repair engineers of cultural properties, constructing or repairing within
the total amount of less than 20 million Korean won or in the area of less than 330m2 building. |
 |
Household Service |
 |
Agriculture, forestry (except lumbering), fishery, hunting industry of non-corporation business of maximum
of 5 regular workers. | | | |
 |
Terms of Insurance : Within 15 days of valid date of the labor contract
 |
If not applied, must pay penalty upto 5 million Korean won. | |
 |
Insuring workers and insurance claims
| - |
Insure by providing delayed payment more than the amount decided by the Minister of Labor(2million
korean won). |
| - |
In case employers delay in payment, foreign workers may report it to a labor inspection office
of the Ministry of Labor, receive a confirmation about such a delay and claim insurance money from HRD Korea | |
 |
Also, foreign workers are eligible for 4 major social insurances just like native Koreans |
| < Accident Compensation Insurance > |
 |
Subject : Industry possessing 1 or more regular workers
(For agriculture, forestry (except
lumbering), fishery, hunting industry with 5 or more regular workers)
?No relations to name or form of employment such
as regular worker, daily worker, temporary employment etc.
| - |
Total construction price of over 20 million Korean won (Including construction price of less
than 20 million Korean won due to alternation in the contract) | |
| < National Health Insurance > |
 |
Applied for the foreign worker employers and foreign workers according to the law of National
Health Insurance. |
 |
Subject : Industry possessing 1 or more regular workers
(For agriculture, forestry (except
lumbering), fishery, hunting industry with 5 or more regular workers) |
| < National Pension>(Principle of reciprocity) |
 |
According to the principle of reciprocity, national pension is applied to foreign workers
from countries that apply it to foreign workers
| - |
Therefore, foreign workers of sending countries under the EPS must subscribe to the national
pension and the pension is not applied to workers from Vietnam. |
| - |
According to the principle of reciprocity, foreign workers from Sri Lanka, Indonesia, and Thailand are
provided with a lump sum payment when they depart. | | | | |
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
M-W 11:30
|
|